

On the most precise of resistors, a 6 th band may be present. This shifts the position of the multiplier and tolerance band into the 4 th and 5 th position as compared to a typical four-band resistor. More commonly, there are five-band resistors that are more precise due to a third significant figure band. It is also possible to have a 5 th band that is the temperature coefficient, which indicates the change in resistance of the component as a function of ambient temperature in terms of ppm/K. For example, components that are made to military specifications are typically four-band resistors that may have a fifth band that indicates the reliability of the resistor in terms of failure rate percentage per 1000 hours of service. Reliability, temperature coefficient, and other variations:Ĭoded components have at least three bands: two significant figure bands and a multiplier, but there are other possible variations. This means that the value 52 MΩ can vary by up to 5% in either direction, so the value of the resistor is 49.4 MΩ - 54.6 MΩ. The gold band in this example indicates a tolerance of ±5%, which can be represented by the letter J. This is a percentage by which the resistor value can vary. The fourth band is not always present, but when it is, represents tolerance. This multiplier is multiplied by the significant figures determined from the previous bands, in this case 52, resulting in a value of 52,000,000 Ω, or 52 MΩ. Using the table, the multiplier is thus 1,000,000. Using the table provided below, the green band represents the number 5, and the red band is 2. For this example, refer to the figure above with a green, red, blue, and gold band. In a typical four-band resistor, the first and second bands represent significant figures. Other possible resistor variations will be described after. In the explanation below, a four-band resistor (the one specifically shown below) will be used. In a typical four-band resistor, there is a spacing between the third and the fourth band to indicate how the resistor should be read (from left to right, with the lone band after the spacing being the right-most band).
Which of these the color refers to is dependent on the position of the color band on the resistor.
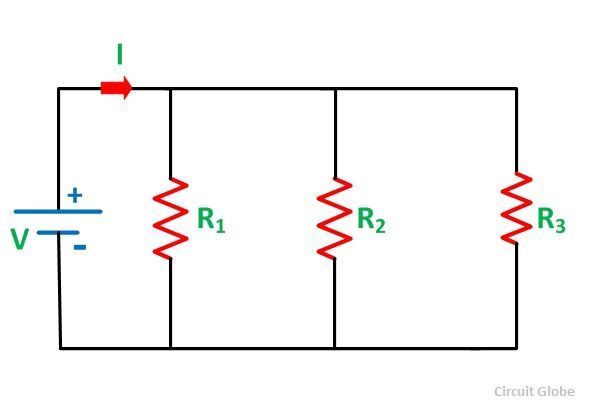
Parallel resistance code#
The resistor color code shown in the table below involves various colors that represent significant figures, multiplier, tolerance, reliability, and temperature coefficient. The color coding for resistors is an international standard that is defined in IEC 60062. Only resistors are addressed by this calculator. Electronic color codes are also used to rate capacitors, inductors, diodes, and other electronic components, but are most typically used for resistors. Length:Īn electronic color code is a code that is used to specify the ratings of certain electrical components, such as the resistance in Ohms of a resistor. This calculator assumes the conductor is round. Use the following to calculate the resistance of a conductor.
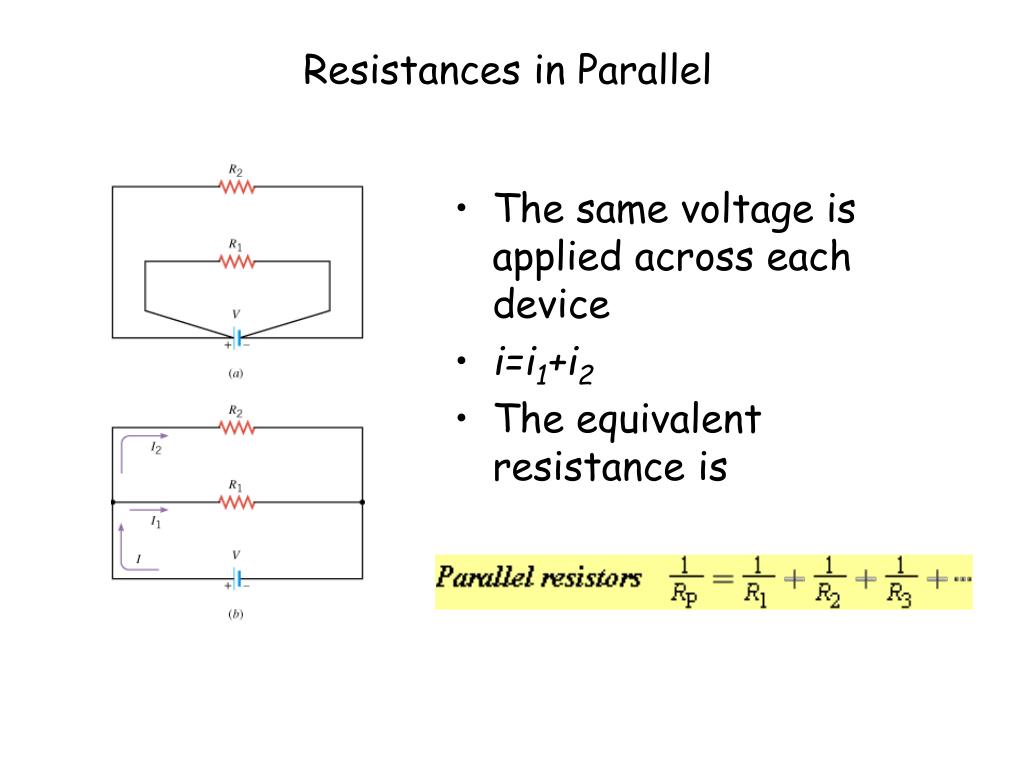
Parallel resistance series#
Provide all of the resistance values in series separated by a comma "," and click the "Calculate" button to determine total resistance. Because, the magnitude of current flowing through inductor and capacitor is equal to Q times the input sinusoidal current I.Provide all of the resistance values in parallel, separated by a comma "," and click the "Calculate" button to determine total resistance. Note − Parallel resonance RLC circuit is called as current magnification circuit. This entire combination is in parallel with the input sinusoidal current source. Here, the passive elements such as resistor, inductor and capacitor are connected in parallel. Consider the following parallel RLC circuit, which is represented in phasor domain. If the resonance occurs in parallel RLC circuit, then it is called as Parallel Resonance. Now, let us discuss parallel resonance in RLC circuits. In the previous chapter, we discussed the importance of series resonance. Electrical Quantity Division Principles.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
